kentoh - Fotolia
Why is the ASAP implementation methodology critical for ECC?
Unlike the Agile approach of project management with its shorter timelines, the Waterfall approach of project management for SAP ECC takes a longer approach to ensure success.
ASAP stands for Accelerated SAP, and the ASAP implementation methodology is intended to optimize the implementation of SAP software.
Implementing SAP ERP Central Component (SAP ECC) is a major undertaking and requires an SAP-focused project implementation methodology to ensure the success of the ECC project. ASAP is the de facto methodology used for SAP ECC and follows the Waterfall approach to project management.
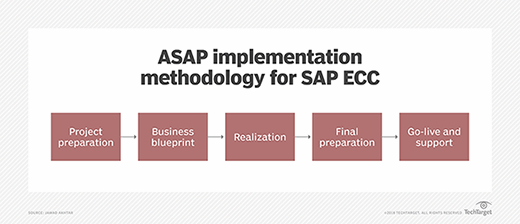
Here are the five phases of the ASAP implementation methodology.
Project preparation
Using the ASAP implementation methodology, in this SAP ECC implementation phase, SAP consultants give initial training to the new SAP ECC business users to give them an overarching view of how SAP ECC works. The business users explain their existing business processes (known as as-is), the business pains they suffer and the current gaps and shortcomings that they'd like SAP ECC to address.
Business blueprint
In this phase of the SAP ECC implementation project, a detailed documentation of the business requirements takes place. The as-is processes are remodeled to fit SAP ECC processes (known as to-be), and a gap analysis helps to evaluate the gaps between the current as-is and SAP ECC's to-be and how best to address these gaps. Some ways to fill the gaps are to develop customized solutions or connect the existing solutions with SAP ECC through an interface. There is also an option to continue certain processes as they are currently being done.
Realization
In this phase using the ASAP implementation methodology, the configuration and development of ECC occur using the documented blueprint of business requirements (the second phase of ASAP) and any functional specifications for customizations.
Final preparation
In this phase with the ASAP implementation methodology, the appropriate players conduct the detailed steps required prior to the system going live. These steps include transporting the configured objects, performing data conversion and upload and handling other manual processes, such as cutover of inventory and financial balance uploads. All these activities and steps take place in the ECC system that the business users will rely on for performing their day-to-day business functions.
Go-live and support
SAP ECC is now live, and business users begin performing business transactions, such as creating sales and purchase orders and receiving goods in the warehouse, and do so in a completely integrated environment. In other words, when a sales order is created, it is followed by delivery of products to the customer and, finally, billing the customer for the delivered products.
The figure below lists the five sequential phases of the ASAP methodology for SAP ECC implementation.